R&D(research and development)经费投入是反映城市科技创新能力的关键指标。收集杭州等10城市2015年R&D投入的相关数据,选取R&D经费投入占GDP比重、政府科技拨款占当地财政支出比重、企业R&D经费支出占主营业务收入比重和第三产业产值比重等指标进行多因素聚类分析,从而找出与杭州市具有相似特征的城市。据此借鉴相关城市R&D投入的经验,以期为杭州市进一步提升R&D投入提供参考。
R&D(research and development)investment is the key index to reflect the ability of urban science and technology innovation. This paper collected the R&D investment data of Hangzhou and other nine cities in 2015, and selected the following indicators to carry out the multifactor cluster analysis: the proportion of R&D investment in GDP, the proportion of government funding for science and technology in local financial expenditure, the proportion of R&D expenditure in enterprises and the proportion of output value of the tertiary industry, with a view to finding cities with similar characteristics to Hangzhou. Accordingly, drawing on the experience of R&D investment in related cities, this paper provides references for further upgrading R&D investment in Hangzhou.
科技创新能力是衡量经济发展水平的重要指标,可以用R&D(research and development)经费投入占GDP比重来表示[1]。R&D经费投入占GDP比重(以下简称R&D投入)已受到广泛关注,例如:蒋惠凤[2]采用聚类分析法,通过对江苏省主要城市投入状况的比较分析发现,在科技投入方面常州与南京、苏州类似; 陶晓懿[3]对区域R&D投入和产出进行聚类分析,提出合理配置资源和提高产出效率的对策; 迟国泰等[4]通过建立科技评价模型,对样本城市数据进行整合,从而归纳出相似省份的发展特征; 赵庆等[5]通过对中国R&D投入现状进行分析,针对“十三五”规划目标提出对策; 王洁[6]从宏观和微观两方面分析了R&D投入现状,并就企业和政府分别提出对策建议; 沈欣[7]、丁魁礼等[8]从政府R&D投入方面入手,分析其现存问题及影响因素并提出对策建议。此外,杨莹[9]、程美华[10]、金雪军等[11]以单个城市为例对政府科技投入进行研究。综上所述,对R&D投入的研究取得了许多成果。根据《杭州市科技创新“十三五”规划》,到2020年杭州市全社会研究与试验发展经费支出占生产总值的比重达到3.5%的目标,为了确保该目标的顺利实现,杭州市应借鉴其他城市的经验。为此,笔者选取了国内R&D投入名列前茅的10城市,将这些城市进行多因素聚类分析,找出与杭州市在产业结构方面具有相似特征的城市,以确保R&D投入具备可比性。据此借鉴相关城市R&D投入的经验,为杭州市进一步提升R&D投入提供参考。
1 聚类分析原理和指标选取1.1 聚类分析原理R&D投入的聚类分析可以有效避免评价中主观性过强的危险。这对杭州市创新投入的精准定位,制定针对性强的政策保障体系是十分重要的。聚类分析原理是将一组对象(抽象或物理)集合到一起,通过不断的分组,最终形成不同的类,组成一类的对象具有相似性[12-14]。由于Ward法具有同类样本的离差平方和较小、类与类的离差平方和较大的优点,因此本文采用Ward法,类间距离的衡量指标为欧氏距离,其公式如下:
dij=[∑Tn=1(xi,tn-xj,tn)2]1/2。
式中:xi,tn表示tn时刻第i个目标的值; di,j表示第i个目标和第j个目标之间的差距,其值越接近于0,说明其相似程度越接近。
1.2 指标选取为了对R&D投入进行聚类分析,一方面引入R&D投入的测度指标R&D投入比重和政府科技拨款占当地财政支出比重(以下简称财政支出比重),另一方面引入反映城市产业特征和企业自主投入特征的测度指标第三产业产值比重和企业R&D经费支出占主营业务收入比重(以下简称企业R&D投入比重)[15]。
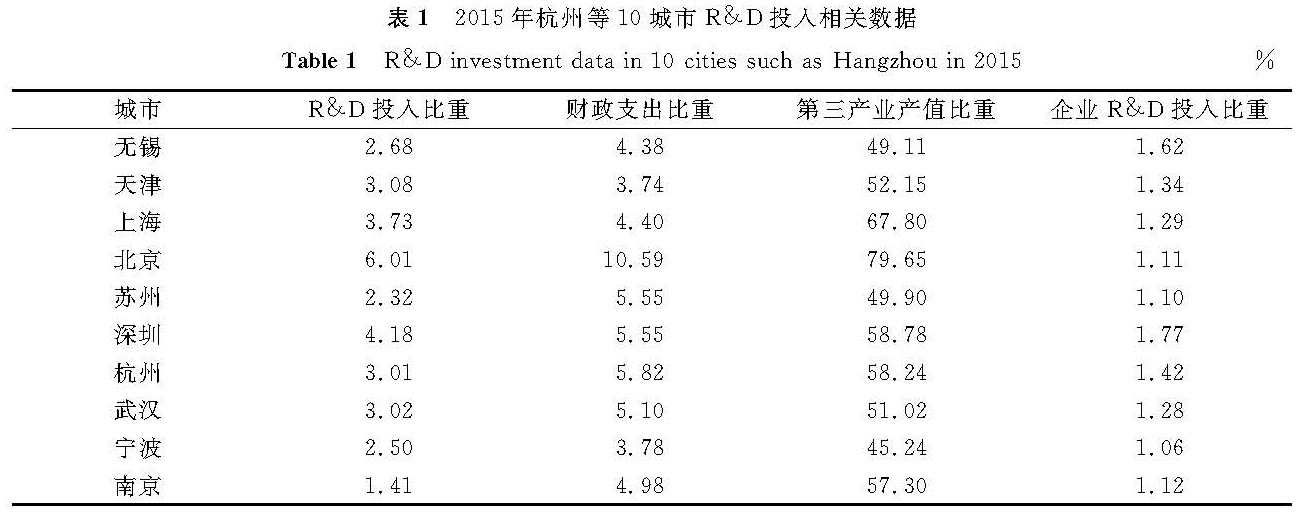
2 杭州等10城市R&D投入的多因素聚类分析2.1 R&D投入比重与财政支出比重的多因素聚类2015年杭州等10城市R&D投入相关数据如表1所示。
数据来源:《2016年杭州市统计年鉴》等10城市统计年鉴。
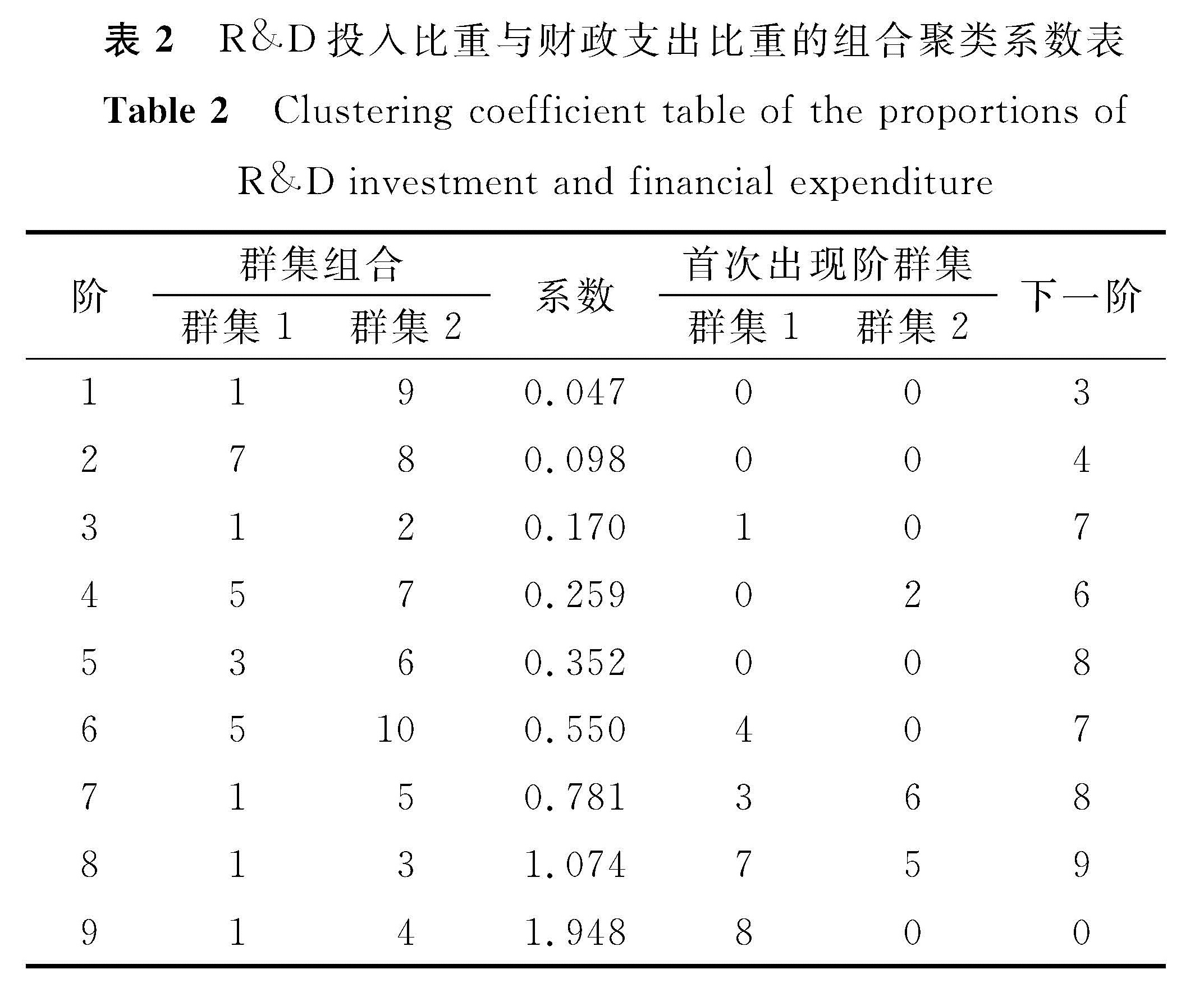
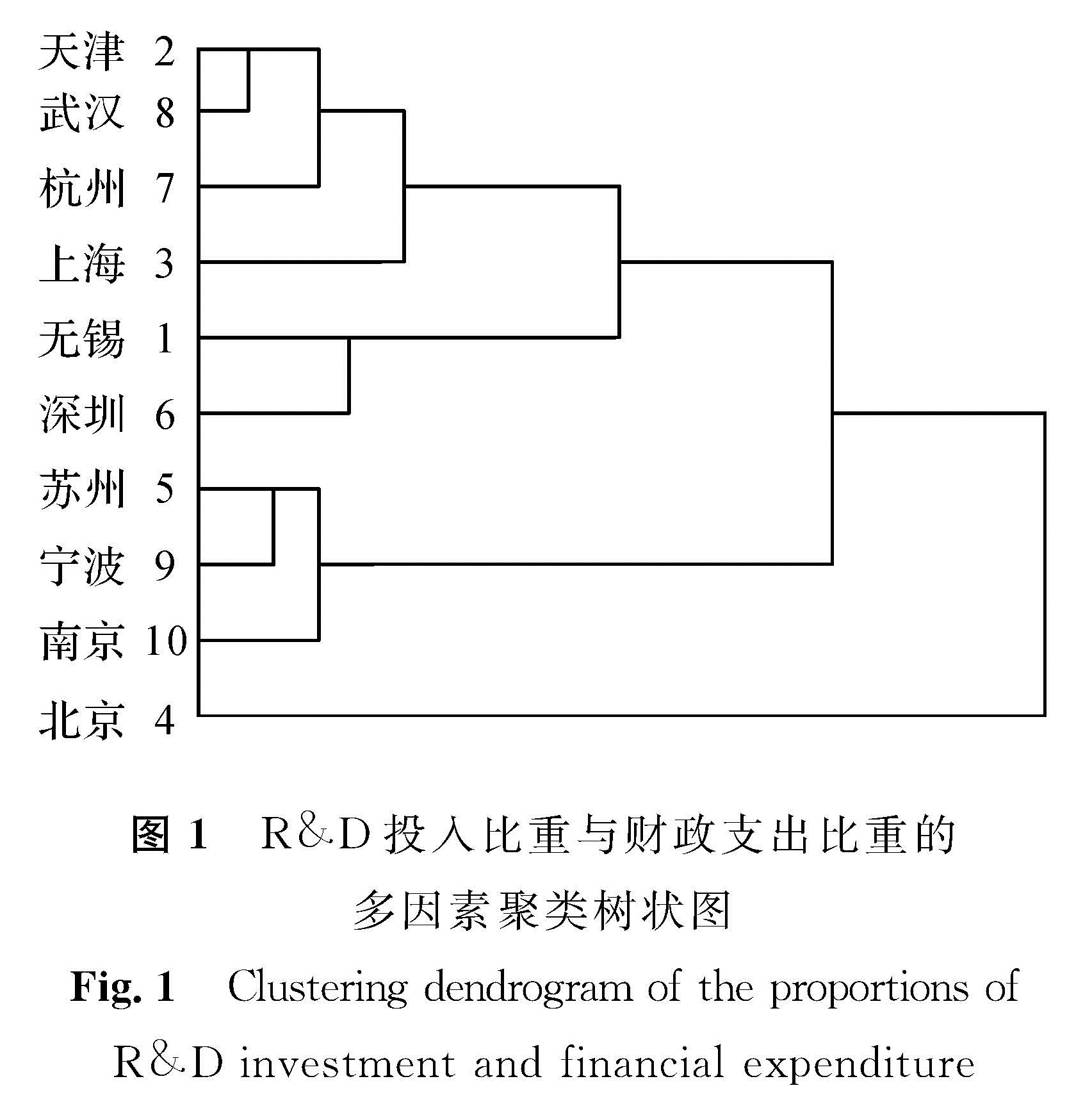
R&D投入比重和财政支出比重是反映创新经费投入的重要指标[16]。要想了解杭州与哪些城市在创新投入方面最相似,可利用相关数据进行聚类分析。采用SPSS 24.0软件对上述10城市的R&D投入水平进行聚类分析,从而掌握这些城市R&D投入的差异。R&D投入比重与财政支出比重的多因素聚类系数如表2所示。最先合并为一类的是阶为1和9的城市,即无锡和宁波,说明这两者在R&D经费投入方面最相似; 第2步合并为一类的是阶为7和8的城市,即杭州和武汉,依此类推,聚类树状如图1所示。将10城市分成4类:北京自成一类; 上海、天津、武汉、杭州同属一类; 深圳、无锡属于一类; 南京、宁波、苏州同属一类。
表2 R&D投入比重与财政支出比重的组合聚类系数表
Table 2 Clustering coefficient table of the proportions of R&D investment and financial expenditure
图1 R&D投入比重与财政支出比重的多因素聚类树状图
Fig.1 Clustering dendrogram of the proportions of R&D investment and financial expenditure
2.2 R&D投入比重、财政支出比重及第三产业产值比重的组合聚类
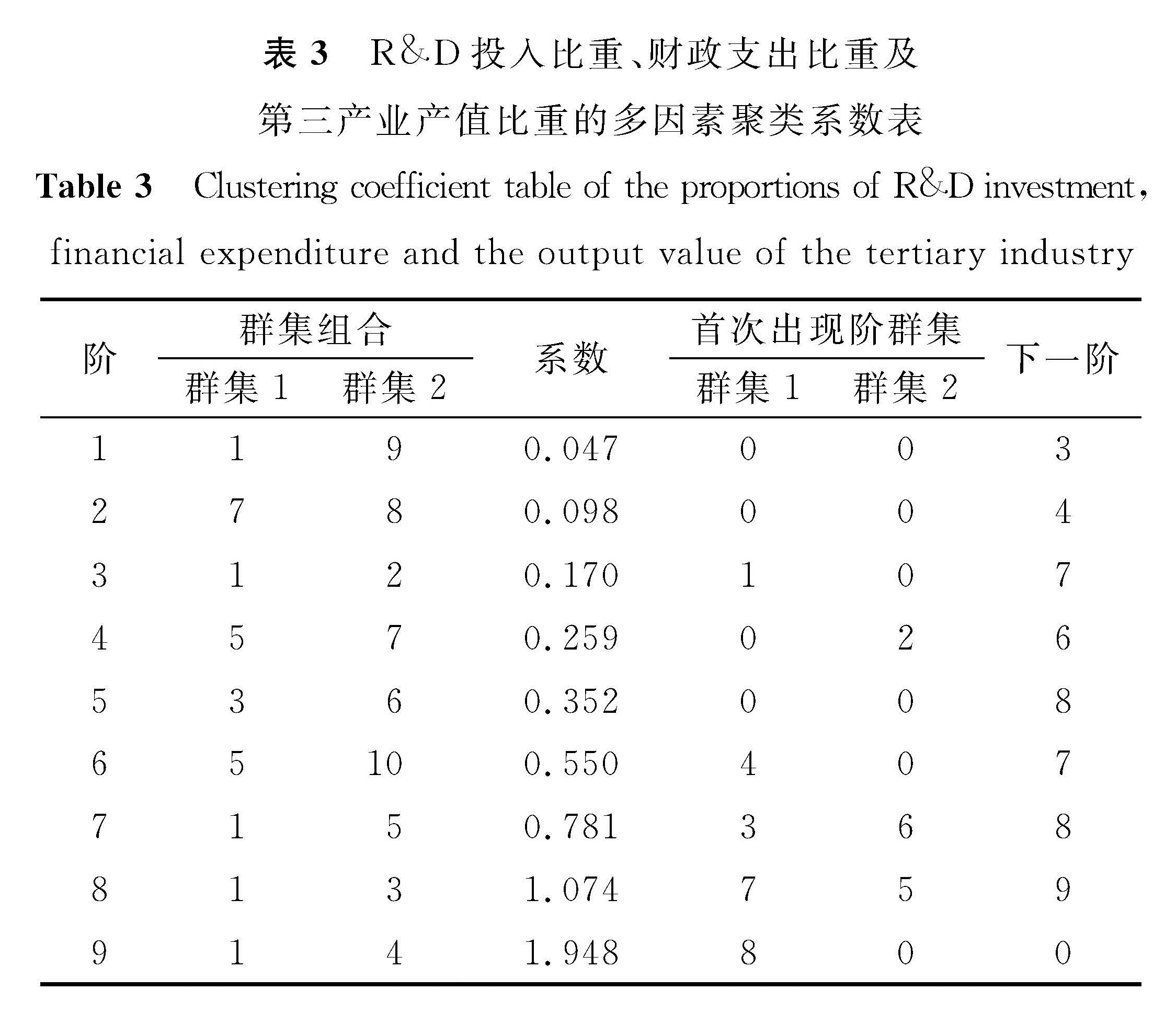
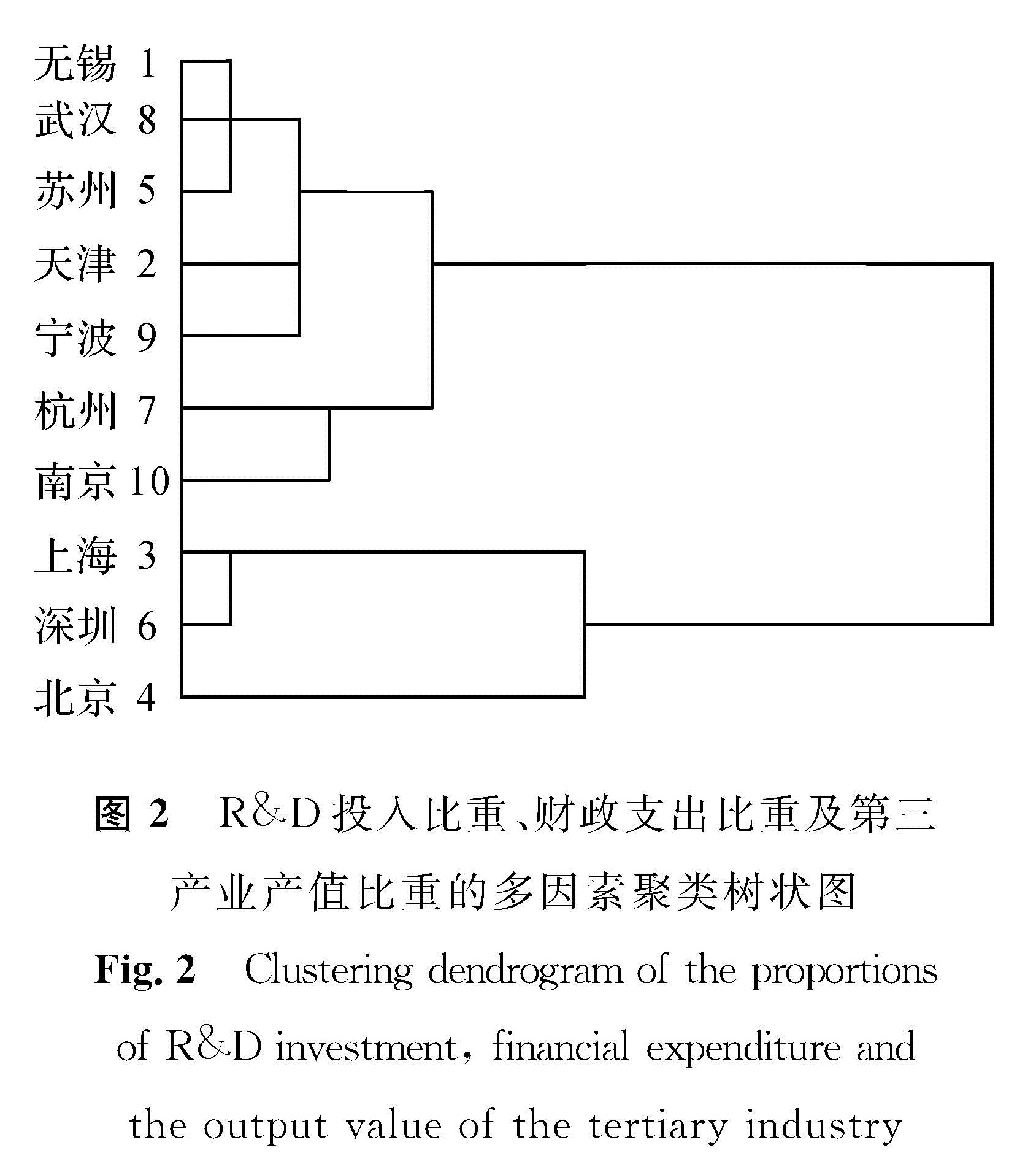
在R&D投入比重与财政支出比重多因素聚类的基础上,结合城市产业特点,增加第三产业产值比重这一指标,进行进一步的多因素聚类分析。3项指标的多因素聚类系数如表3所示,多因素聚类树状如图2所示。由图2可知,当增加第三产业产值比重时,城市的分类会产生相应变化:北京仍然自成一类; 深圳、上海同属一类; 南京、武汉、杭州、苏州同属一类; 天津、宁波、无锡同属一类。
表3 R&D投入比重、财政支出比重及第三产业产值比重的多因素聚类系数表
Table 3 Clustering coefficient table of the proportions of R&D investment,financial expenditure and the output value of the tertiary industry
图2 R&D投入比重、财政支出比重及第三产业产值比重的多因素聚类树状图
Fig.2 Clustering dendrogram of the proportions of R&D investment, financial expenditure and the output value of the tertiary industry
2.3 R&D投入比重、财政支出比重、第三产业产值比重及企业R&D投入比重的多因素聚类
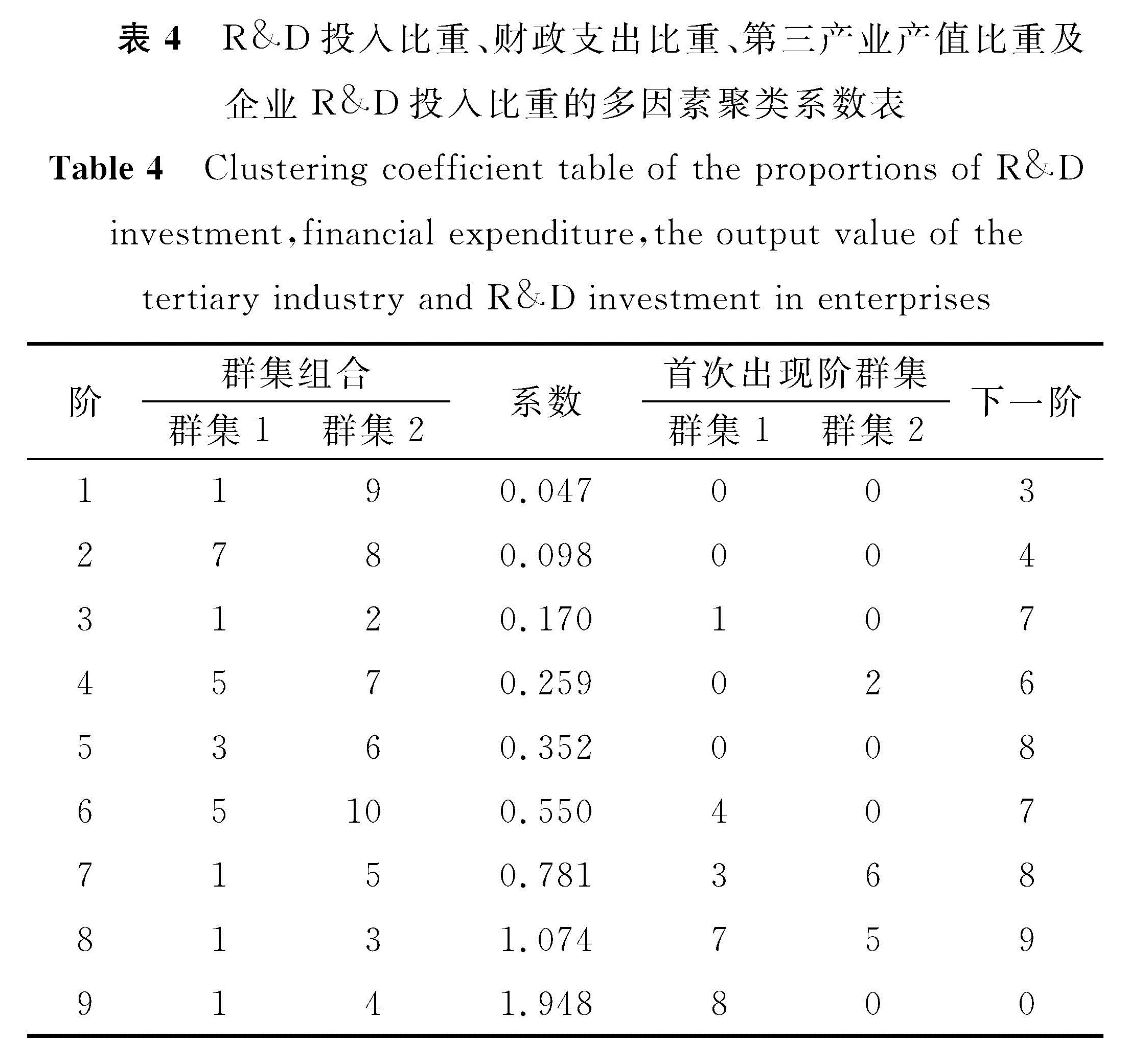
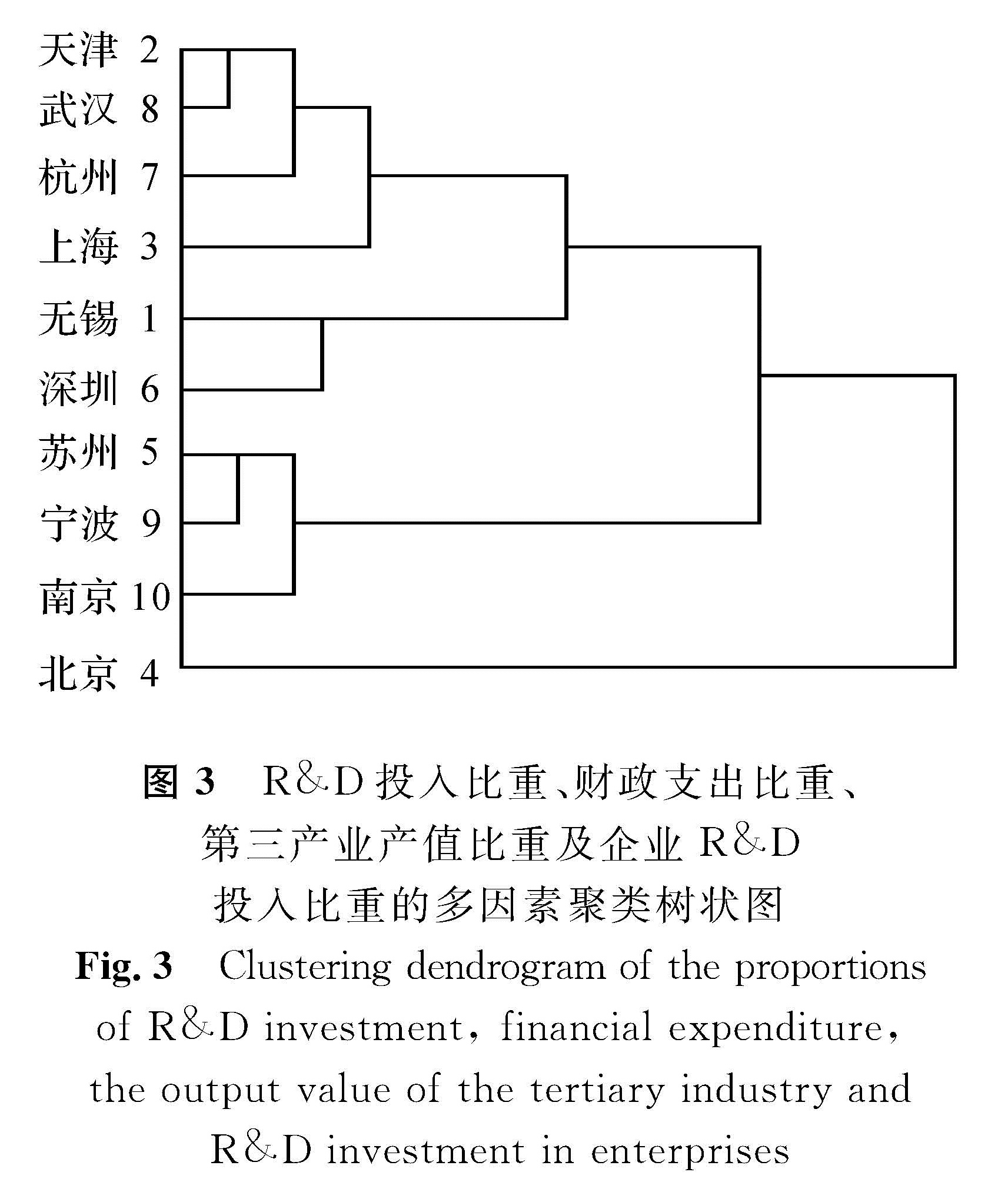
在以上3项指标的基础上,增加企业R&D投入比重的指标作聚类分析。R&D投入比重、财政支出比重、第三产业产值比重与企业R&D投入比重的多因素聚类系数和聚类树状如表4和图3所示,由此可见:北京仍自成一类; 南京、宁波、苏州同属一类; 上海、杭州、武汉、天津同属一类; 深圳、无锡同属一类。
表4 R&D投入比重、财政支出比重、第三产业产值比重及企业R&D投入比重的多因素聚类系数表
Table 4 Clustering coefficient table of the proportions of R&D investment,financial expenditure,the output value of the tertiary industry and R&D investment in enterprises
图3 R&D投入比重、财政支出比重、第三产业产值比重及企业R&D投入比重的多因素聚类树状图
Fig.3 Clustering dendrogram of the proportions of R&D investment, financial expenditure,the output value of the tertiary industry and R&D investment in enterprises
2.4 杭州多指标组合聚类的结果
由R&D投入比重、财政R&D支出比重的二因素进行组合聚类,得出杭州、武汉、天津、上海同属一类。其中,杭州R&D投入比重均低于其他3城市,而财政R&D支出比重均高于其他3城市。由R&D投入比重、财政R&D支出比重、第三产业产值比重的三因素进行组合聚类,得出杭州、武汉、南京、苏州同属一类。其中,杭州R&D投入比重略低于武汉,而高于苏州、南京; 在财政R&D支出比重及第三产业产值比重两方面杭州均高于其他3城市。由R&D投入比重、财政R&D支出比重、第三产业产值比重、企业R&D投入比重的四因素进行组合聚类,得出杭州、武汉、天津、上海同属一类。其中,杭州R&D投入比重低于其他3城市; 第三产业产值比重仅次于上海外,高于其他2城市; 杭州财政R&D支出比重、企业R&D投入比重均高于其他3城市。
3 结 语本文以杭州等10城市2015年科技投入相关统计数据为基础进行多因素聚类分析,R&D投入特征、城市产业特征和企业自主投入特征的多因素聚类结果显示,与杭州最为相近的城市为武汉,其次为天津、上海,再次为南京和苏州。从实际情况看,杭州与北京在产业结构、财政支出比重等指标上相差较大,明显不可比。而杭州与武汉同为副省级城市,在产业结构、企业R&D投入比重等指标上比较相近,尤其是近几年武汉的财政R&D投入增速很快。因此,杭州可借鉴武汉的先进经验进一步挖掘科技投入的潜力或新途径,例如:进一步增加财政R&D支出,充分发挥财政资金的杠杆作用,制定有效的激励政策,引导企业增加R&D投入; 引进高层次人才,构建高层次研发基地,提升高层次科研投入等。
- [1] 房立波.浙江R&D经费投入分析[J].科技管理研究,2014(18):107.
- [2] 蒋惠凤.常州科技投入现状及其在省内的聚类分析[J].常州工学院学报,2015,28(4):48.
- [3] 陶晓懿.区域R&D资源投入和产出差异聚类及趋势分析[J].科技进步与对策,2010,27(17):35.
- [4] 迟国泰,顾雪松,王卫.基于关联分析的科技评价模型及典型省份实证[J].科研管理,2011,32(1):68.
- [5] 赵庆,杨立男.新常态下增加我国R&D经费投入对策探析[J].中国乡镇企业会计,2015(9):74.
- [6] 王洁.R&D投入现状及对策分析[J].中国电子商务,2013(17):200.
- [7] 沈欣.政府科技投入问题的研究综述[J].科技风,2013(12):243.
- [8] 丁魁礼,张云娣,杨芳.珠三角政府科技投入规模和强度的比较研究[J].科技管理研究,2014(14):91.
- [9] 杨莹,瞿肖怡.苏州市R&D经费投入现状与分析[J].天津科技,2016,43(2):13.
- [10] 程美华.政府科技投入情况及存在问题分析:以杭州市为例[J].今日科技,2008(7):47.
- [11] 金雪军,许杭.杭州市政府科技投入绩效评估体系研究[J].杭州科技,2006(2):15.
- [12] 王冰,王皓.基于聚类分析的我国财政支出结构省际比较研究[J].经济与管理,2014,238(3):44.
- [13] 党耀国,侯荻青.基于特征提取的多指标面板数据聚类方法[J].统计与决策,2016(19):68.
- [14] 范雅静.基于城市消费水平多指标面板数据的聚类分析研究[J].科技广场,2015(1):145.
- [15] 成力为,张东辉,郭园园.辽宁省工业企业研发投入强度及结构特征分析:基于辽宁省1.5万及全国30万个工业企业样本比较[J].金融理论与教学,2014(6):57.
- [16] 王莉.R&D投入对经济增长的影响研究:基于我国数据分析[D].济南:山东财经大学,2016.
 图 1 R&D投入比重与财政支出比重的多因素聚类树状图
Fig.1 Clustering dendrogram of the proportions of R&D investment and financial expenditure
图 1 R&D投入比重与财政支出比重的多因素聚类树状图
Fig.1 Clustering dendrogram of the proportions of R&D investment and financial expenditure